Weekly cases of Hand Foot Mouth Disease in Singapore at highest in 2.5 years. It was a huge jump as compared to the same period during last year. What exactly is Hand Foot And Mouth In Children (HFMD)?
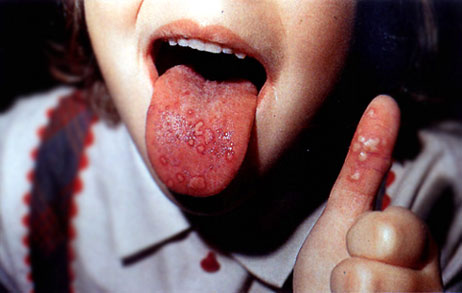
What is HFMD?
Hand-foot-and-mouth disease (HFMD) is a common viral illness affecting infants and young children. It is spread from person to person by direct contact with the nasal discharge, saliva, faeces, sweat and fluid from the rash of an infected person. HFMD occurs mainly in children under 10 years old (especially children under 5 years old) but can also occur in adults. Children are more likely to be at risk for infection and illness because they are less likely than adults to have antibodies to protect them.
Although it is usually a mild disease, it has been associated with fatalities usually due to complications involving the heart and nervous system.
What is the cause of it?
HFMD is caused by viruses that belong to the enterovirus genus (group).
This group of viruses includes polioviruses, coxsackieviruses, echoviruses and enteroviruses.
What are the symptoms of HFMD?
(Some symptoms vary from individuals)
- Fever
- Vomiting
- Fatigue
- General discomfort or uneasiness
- Sore throat
- Painful oral lesions
- Irritability in infants and toddlers
- Non-itchy body rash
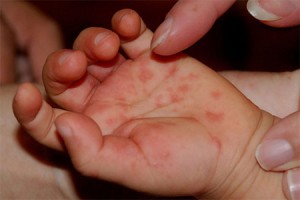
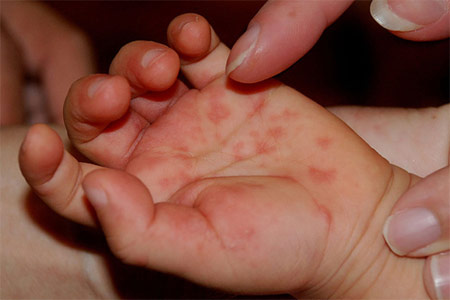
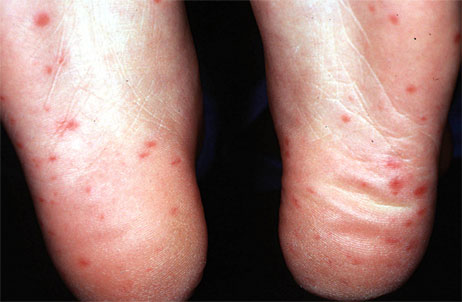
- Red spots or blisters on palms of hands and soles of feet
- Oral ulcer
- Sores or blisters may be present on the buttocks of small children and infants
- Loss of appetite.
Is there any treatment?
There is no specific treatment for HFMD. Treatment and medication subscribe by the doctor only provide relief from fever, aches and pain.
The common incubation period (the time between infection and onset of symptoms) is from five to seven days. During this period of time, individual affected with HFMD is advisable to stay at home and get lots of rest.
Advice for parents!
- Parents are strongly advised to consult a doctor early if their child has symptoms of HFMD.
- Look out for any change in your child’s normal behaviour.
- Children should be kept away from crowded public places (such as schools, malls, markets and public transport) if they show signs of infection.
- Avoiding close contact (kissing, hugging, sharing eating utensils or cups, etc.) with individuals with HFMD.
- Clean dirty surfaces and soiled items like toys, first with soap and water and then disinfecting them with disinfectants.
- Good hygiene practices lower the risk of infection. Family members are advised to follow good hygiene practices, including frequent hand washing, to limit the spread of the infection.
- If your child is infected with HFMD, it is important that they stay at home and get lots of rest.
*Hand Foot Mouth Disease images courtesy of KK Women’s and Children’s hospital Singapore
Want more comprehensive info? Check out our e-guides here.
Like what you see here? Get parenting tips and stories straight to your inbox! Join our mailing list here.