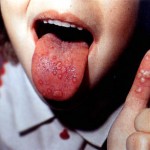
HFMD is a common, highly contagious viral infections that usually begins in the throat. Common causes of HFMD are Coxsackie Virus A and Enterovirus 71.
Transmission:
These viruses spread via direct contact with nose and throat discharges, saliva, fluid from blisters or the stools of an infected person. Young children below five years are particularly susceptible.
The disease is most contagious the first week of the disease. The time between infection and the development of symptoms is about 3 – 7 days.
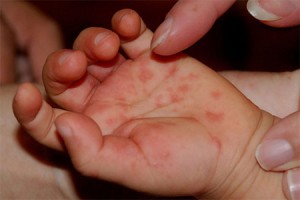
Symptoms
- Fever
- Loss of appetite
- Sore throat, drooling
Signs
- Ulcers that occur primarily in the mouth, inside the cheeks, tongue and back of throat.
- Rash that affects hands and feet. Buttocks and genitalia may exhibit similar rash.
Who are prone to infections?
Young children and infants who have no immunity to these viruses and whose personal hygiene habits further the spread of the virus via the oral-fecal route
Where are you at risk for infections?
- Crowding areas such as in daycare centers, kindergartens, schools or any places that children congregate
- Poor sanitary areas
 When is it a concern?
When is it a concern?
You should seek medical attention if:
- A high fever is not reduced by medication
- Signs of dehydration occur
- Lethargy
- Decreased or dark urine
- Persistent irritability and/ pain in the neck.
- Seizures
Treatment:
There is no treatment for HFMD. The disease has to run its course. Antibiotic is not useful and not indicated for the treatment of HFMD.
Acetaminophen or ibuprofen can be used to ease painful mouth sores or discomfort associated with fever. Oral aid drops or gel can be dabbed onto sores to alleviate pain. Cold foods like ice cream and popsicles ease pain by numbing the area.
Prevention:
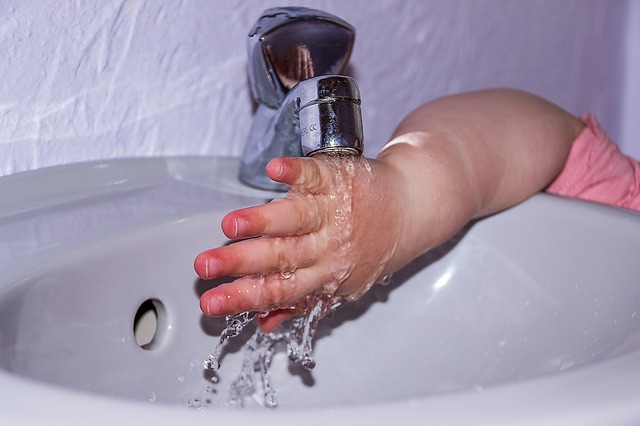
There is no vaccine to prevent HFMD. Hand washing is the best protection. Remind everyone in your family to wash their hands frequently, particularly after using the toilet, changing a diaper, before meals, and before preparing food. Shared toys in daycare centers should be routinely cleaned with a disinfectant because these viruses can live on objects for several days.
By Dr Ratna Sridjaja
Paediatrician
SBCC Baby & Child Clinic
Practice Address:
SBCC Baby & Child Clinic (Gleneagles)
6 Napier Road #07-01/03 Gleneagles Medical Centre
Singapore 258499
Tel: 6235 6706/ 6397 6966 (Hotline)
Email: info@sbcc.sg
If you find this article useful, do click Like and Share at the bottom of the post, thank you.
Want more comprehensive info? Check out our e-guides here.